sigmafullpac
Drivers Of Globalisation Yip
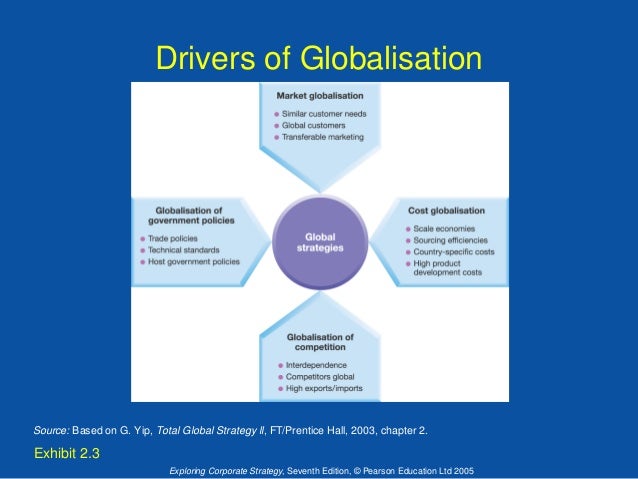
ContainerisationThe costs of ocean shipping have come down, due to containerisation, bulk shipping, and other efficiencies. The lower unit cost of shipping products around the global economy helps to bring prices in the country of manufacture closer to those in export markets, and it makes markets more contestable globallyTechnological changeRapid and sustained technological change has reduced the cost of transmitting and communicating information – sometimes known as “the death of distance” – a key factor behind trade in knowledge products using web technologyEconomies of scaleMany economists believe that there has been an increase in the minimum efficient scale (MES) associated with some industries. If the MES is rising, a domestic market may be regarded as too small to satisfy the selling needs of these industries. Many emerging countries have their own transnational corporationsDifferences in tax systemsThe desire of businesses to benefit from lower unit labour costs and other favourable production factors abroad has encouraged countries to adjust their tax systems to attract foreign direct investment (FDI). Many countries have become engaged in tax competition between each other in a bid to win lucrative foreign investment projects.Less protectionismOld forms of non-tariff protection such as import licensing and foreign exchange controls have gradually been dismantled. Borders have opened and average import tariff levels have fallen.That said, it is worth knowing that, in the last few years, there has been a rise in non-tariff barriers such as import quotas as countries have struggled to achieve real economic growth and as a response to persistent trade and current account deficits.Growth Strategies of Transnational and Multinational CompaniesIn their pursuit of revenue and profit growth, increasingly global businesses and brands have invested significantly in expanding internationally.
This is particularly the case for businesses owning brands that have proved they have the potential to be successfully globally, particularly in faster-growing economies fuelled by growing numbers of middle class consumers.
DIAGNOSING INDUSTRY GLOBALIZATION POTENTIAL(Excerpts from G. Yip’s Total Global Strategy)Industry globalization drivers are the underlying conditions in each industry that create the potential for using global strategy.
Here we will examine each driver in more depth.To achieve the benefits of globalization, the managers of a worldwide business need to recognize when industry conditions provide the opportunity to use global strategy levers. These industry conditions can be grouped in four categories of globalization drivers: market, cost, government, and competitive. Each key industry globalization driver affects the potential use of global strategy levers (global market participation, global products. That is why it is important to understand how industry globalization drivers affect the threat of entry and rivalry among existing competitors.MARKET GLOBALIZATION DRIVERSMarket globalization drivers-common customer needs, global customers, global channels, transferable marketing, and lead countries-depend on the nature of customer behavior and the structure of channels of distribution. These drivers affect the use of all five global strategy levers. As illustrated in Exhibit 2-1, different industries have different levels of market globalization drivers.
These comparative rankings are approximate only and will also change with time.Common Customer NeedsCommon customer needs represent the extent to which customers in different countries have the same needs in the product or service category (or the group of products and services) that defines an industry. Many factors affect whether customer needs are similar in different countries. These factors include whether differences in economic development, climate, physical environment, and culture affect needs in the particular product or service category as well as whether the countries are at the same stage of the product life cycle.? Common customer needs particularly affect the opportunity to use the global strategy levers of global market participation, global products and services, and global competitive moves. Common needs make it easier to. 639 Words 3 PagesYIP’S GLOBALIZATION MODELWe have followed George Yip’s famous globalization model (1992) to analyse the forces behind attractiveness of globalization for telecom firms in India and more specifically Bharti Airtel.1.
MARKET GLOBALIZATION FORCESEvery month about 8-10 million subscribers are being added in the Indian mobile database. India is likely to see 80% teledensity (fixed +mobile users) by 2014 and is set to see waning demand there on. (source: Wikipedia.com)Given the current level of saturation. 14466 Words 58 Pages+ 1+2 2= 1+1 1+1 1+2THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN FORWARD RATES AND SPOT RATES(1 yn ) n (1 f n ) (1 yn 1 ) n 1Example: Look at Henry Yip’s Textbook – pg. 38-40fn = one-year forward rate for period n yn = spot rate/yield for a security with a maturity of nSPOT RATES AND TERM STRUCTURE OF ZERO COUPON BONDSThe term structure of coupon bonds may also be used to infer yields to maturity.
3201 Words 13 Pagespart of the company's success. For example, many of the products that welcomed the eastern European market were new, while others were old favorites. It made members of the European market feel like they were getting something special.Yip's ModelYip's Model focuses on globalization and just how international a given company is and has the potential to be. 'Yip argued that, 'the global company does not have to be everywhere but has the capability to go everywhere, deploy any assets and access.
Reason 11 Crack powerful tool for making music. It brings Ableton Link as the latest sync form which you can help it from move section. Reason 7 Crack Keygen Free Download.This keygen that has been well created made available for free. Download Now! Reason 7 crack keygen serial.
2408 Words 10 Pagesanalytical processes of strategic management, whilst using examples of companies such as Apple Inc. And Samsung, to illustrate the implications and outcomes such strategies may have on businesses. To do this I will concentrate on Johnson’s cultural web, Yip’s drivers of internationalisation and Brownman’s strategy clock processes. “The taken-for-granted nature of culture is what makes it centrally important in relation to strategy and the management of strategy” (Johnson et al., 2008, p.196). I have chosen.


1964 Words 8 Pagesinfrastructure, knowledge and low cost laborPresent business models’ economic growth is concealed by the threat of economic velocity of globalization and the advancement and interruption of technical innovation.Global Strategic Management embraces a comprehensive thinking approach to the ‘design of innovative business’ models and the evolution of centralizing strategic procedures that benefit competitive dominance.Contingency framework developed by Yip’s (1989) for the global strategies explains that peripheral. 1048 Words 5 Pagesestablish a good business model that let them compete with Wal-Mart. The vision set by its CEO, Terry Leahy, to develop dense networks of new breed of convenience styled stores.Tesco’s ability to integrate with the local suppliers and bring major supplier to the new markets also helped in to developing “smaller-format stores served by a short lead time integrated food preparation/distribution system”.2.Evaluate Tesco’s International expansion in the context of Yip’s ‘drivers of globalisation’.
Yip 2003
2595 Words 11 PagesTable of content1) Executive Summary.Page 42) Introduction. Page 53) Background of industries Page 54) PESTEL Analyse. Page 65) CAGE Model. Page 76) YIP’s model.
Page 97) ConclusionPage 118) ReferencesPage 12Executive SummaryIn this portfolio I have broke down and clarified about global retail. 1988 Words 8 PagesTITTLE: ‘‘THE AIRLINE INDUSTRY’’ (VIRGIN ATLANTIC AIRLINES)Contents1) Introduction to airline industry 2) Drivers of globalisation using yip’s model 2.1 Market globalisation 2.2 Cost globalisation 2.3 Globalisation of government policies 2.4 Globalisation of competition 3) Localisation- arguments against globalisation 4) Pestle Analysis 5) Porter’s 5 forces analysis and their application to Airline industry 5.1 Rivalry amongst Existing Firms 5.2 Threat of substitution 5.3 Threat. 5185 Words 21 Pagesafter providing a brief overview of strategy context, we are going to analyze and compare some relevant frameworks.Thus, in the one hand, we are going to analyze the Johnson and Scholes’s framework.On the second hand we are going to analyze the Yip’s framework in association wwith the Porter’s framework.And as a final point, after comparing theses frameworks the last part depicts some critical analysis and recommendations.I.AN INTRODUCTION TO STRATEGYThe aim of this part is to define. 1889 Words 8 PagesBusiness Strategy of Virgin Atlantic AirlinesContents1) Introduction to airline industry 2) Drivers of globalisation using yip’s model 2.1 Market globalisation 2.2 Cost globalisation 2.3 Globalisation of government policies 2.4 Globalisation of competition 3) Localisation- arguments against globalisation 4) Pestle Analysis 5) Porter’s 5 forces analysis and their application to Airline industry 5.1 Rivalry amongst Existing Firms 5.2 Threat of substitution 5.3 Threat of new entrants.